TECHNOLOGIES
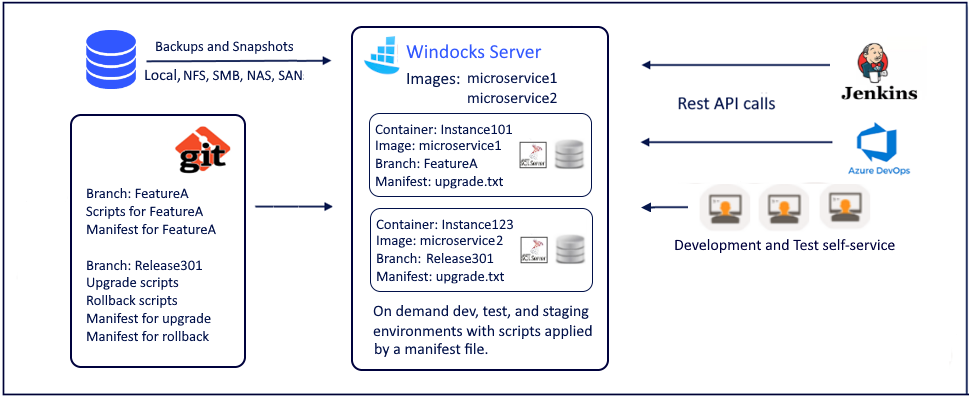
Release migrations (SQL script & Entity Framework) source control & deployments with Git, containers & database clones
Dev/test/staging environments with production data and release SQL scripts or Entity Framework (EF) migrations applied for SQL Server, PostgreSQL, and MySQL
Benefits
- Enhance remote team and #WFH collaboration, with bug reproduction as simple as running a test on a fresh identical cloned environment.
- Build security into the database image, with data masking and encryption. User role based access controls and audit logs support compliance reporting and audits.
- Work with SQL Server, PostgreSQL, MySQL databases.
- All releases and editions of SQL Server 2008 to 2022, with the DB engine, Reporting, Analysis, Integration, and SQL Agent services. PostgreSQL 10, 11, 12, and MySQL releases 5.6, 5.7 and 8.x.
- Reign in VM sprawl with a 4 vCPU server supporting 20 simultaneous environments, with each clone using only 40 MB of storage. Customers average a 50 to 70% reduction in VM sprawl, storage, and license costs.
The Process
- Developers write code and database scripts in their Git branches. Those using EF migrations, generate migrations in their branches
- Developers get containers on demand with production database clones. These containers and clones are long lived during the developer's development phase and used for developing and unit testing
- Developers push code (including SQL scripts or EF migrations) to their Git branch. Now, they get database clones with the migrations automatically applied. Developers can specify which migrations they want automatically applied. Different developers can get different migrations applied on the production database clones
- At some point the developer merges their branch to the current release branch
- The test team and the DevOps pipelines get database containers with database clones and the release scripts or EF migrations from the release branch applied. Testing is done with production data clones and the release scripts or EF migrations applied automatically
- The same scripts or EF migrations are applied to production
- After production release, SQL Server Images are updated incrementally with production transaction log backups and the same process is repeated for the next release
Explore topics
CONCEPTS
Database Orchestration
CONCEPTS
Database DevOps pipelines
CONCEPTS
Databases and Azure DevOps
CONCEPTS
Test Data Management
FEATURES
Database cloning
FEATURES
Database masking
FEATURES
Synthetic data
FEATURES
Access control
TECHNOLOGIES
SQL Server containers
TECHNOLOGIES
SSRS containers
TECHNOLOGIES
Oracle containers
TECHNOLOGIES
Azure SQL dev, test
TECHNOLOGIES