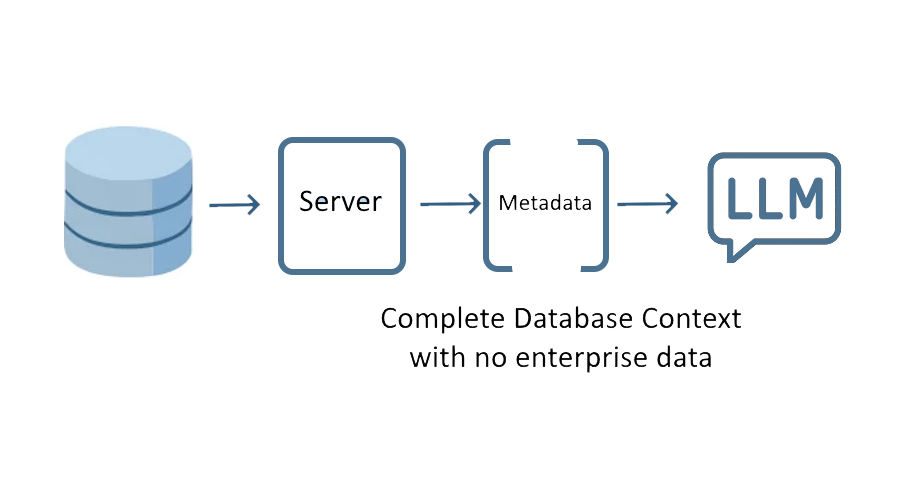
Automated Database Context
Database metadata is served in a form that enables LLMs to comprehend databases, while maintaining enterprise access controls and policies, and with zero data exposure.
LLMs depend on structured context for accuracy, and the LEDGE complete database context enables comprehension to scale to multiple databases within the LLM context window.
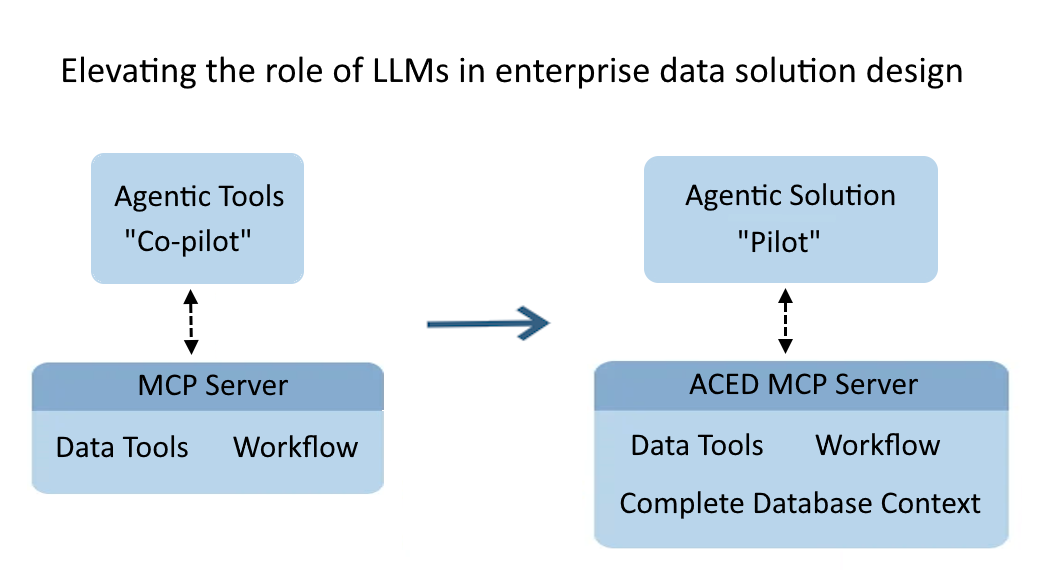
The LLM as "captain" rather than "co-pilot"
LangGrant proves that LLMs can design complex data solutions, by delivering complete and accurate multi-step analytics data plans.
Other MCP servers and agents are limited to vendor tooling, limiting their role to being a “tools co-pilot,” supporting vendor tools and workflows.
LangGrant's complete database context creates the possibility of limitless Agentic solutions.
Real time database context
Databases are dynamic with transactions, updates, and schema changes. A complete database context must also be dynamic, responding to each user query. A real time database context reflects the database at the time of the user query, with context focused for the user query.
Stateful, scalable, real time, and useful database context is achieved by filtering the context to reflect user needs, and with smart caching.
Tools and plan binding
Once the LLM comprehends databases, the LEDGE server binds the LLM to a step-wise analytics data plan that includes cross table and database joins, data cleansing, normalization, statistics, logical features, and other tools. This “tools” binding is discussed in depth in the Plan Orchestration.
Explore more capabilities
Orchestration: automated database context
LEDGE automatically delivers complete database context for LLMs to comprehend multiple databases simultaneously at scale. Like a skilled engineer, once an LLM understands databases it can contribute to solution design.
Orchestration: analytic plan
LEDGE binds LLMs to deliver accurate analytic plans for user queries. Plans are saved, easily validated and modified, and run to deliver analytics data within minutes of the user query.
Governance
PII safeguards, authorization controls, data residency rules, firewall restrictions, and token-governance policies are built-in by design. No sensitive data leaves governed systems.
Plan management
LLM generated plans are saved, easily reviewed and validated, modified, and executed, for LLM use that is transparent, explainable, and repeatable.
Database cloning and containers
On demand database clones with containers provide Agent developers with production database copies (with optional masking) for agentic AI dev/test.

Database subsetting and synthetic data
Database subsetting with synthetic data provides added context for working with complex multi-database environments.