Database Virtualization or Cloning
Database virtualization (also cloning) delivers writable database copies, that occupy minimal storage.
When lower level data environments aren't keeping pace with business needs.
Writable copies of databases are delivered in seconds to new Docker containers or existing database instances, with each copy occupying less than 100 MB. Cloned database environments are ideal for Continuous Integration, database development and test, ETL jobs, reporting, and more.
The benefits of database cloning include:
- Over 95% reduction storage
- Clones of Oracle, SQL Server, Postgre, MySQL, and more
- Faster, more thoroughly tested database updates
- Responsive production debug and support with point-in-time and near real-time production environments
- Compliance with centralized image repo of lower level environments, with security policies built-in.
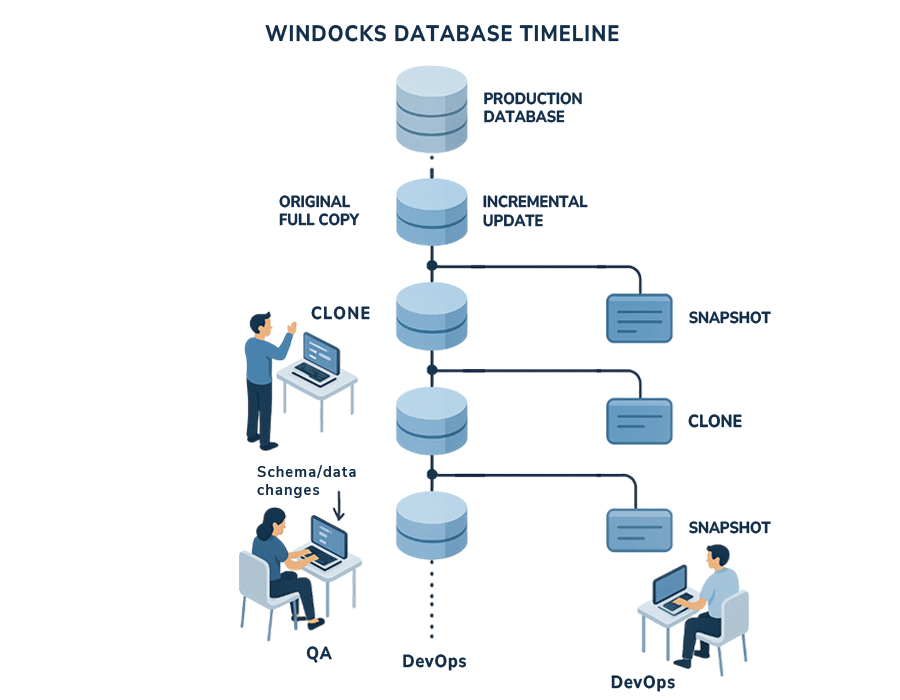
Point-in-time and near real-time databases
Database virtualization is based on a full byte copy of the database(s) in an image, created by restoring backups, database files, or via an Oracle stand-by instance. Images scale to deliver databases up to 50 TB or more, and can include dozens of databases. Data masking, user permissions, Git operations, and other steps are built in, or applied as clones are delivered, ensuring data is ready for use.
Windocks database virtualization supports a “database timeline” and point in time environments on Linux and Windows. Writable snapshots enable a user environment to be saved as a new image and shared with a larger team.
Database refresh
Database refresh is the process of getting incremental changes from the primary / production database and making the current primary / production databases available for testing, development, DevOps, machine learning model test and training. Windocks database refresh is available for SQL Server and Oracle. Build an image once from the full primary databases or backups just once. After that Windocks automatically refreshes the image with incremental changes from primary / production.
Database refresh for Oracle
Windocks provides database refresh for Oracle using an Oracle Docker container that stays in sync with the primary / production. Windocks builds point in time images instantaneously using the synced data in this container. From these point in time images, you may self service Oracle database clones in docker containers or Oracle instances. This unique architecture provides point in time database clones for testing, DevOps, and MLOps without requiring complex infrastructure with staging servers.
Database refresh for SQL Server - video
Windocks delivers 6 powerful capabilities

Database Cloning
Create writable copies of databases in seconds instead of hours. This enables fast development, testing, and analytics, helping teams work efficiently with full, realistic environments without impacting production systems.
SQL Server containers
Run multiple isolated SQL Server instances on a single machine using Docker Windows containers. This maximizes hardware utilization, simplifies testing and deployment, and provides great support for remote teams.
.png?width=60&height=60&name=database%20(2).png)
Synthetic data
Protect sensitive data by replacing Personally Identifiable Information (PII) like names, phone numbers, and addresses with synthetic data that is modeled to reflect source distribution. This ensures compliance with regulatory and enterprise policies, and exposure of real customer data.
Feature Data
Code free data aggregation, cleansing, and enriching from multiple sources to create “features” for Machine Learning and AI. Feature data enables advanced analytics and ML modeling, such as predicting fraudulent transactions, improving decision-making, and driving business outcomes.

Single source of truth
Combine data from multiple databases into a unified “feature data table.” This provides accurate, consolidated information across systems, eliminates duplication, and ensures consistent reporting for analytics, compliance, and business intelligence needs.

Database subsetting
Reduce large databases to smaller, targeted datasets while maintaining all key relationships and integrity between tables. Subsetting helps accelerate testing, minimizes storage requirements, and protects sensitive information during development activities.