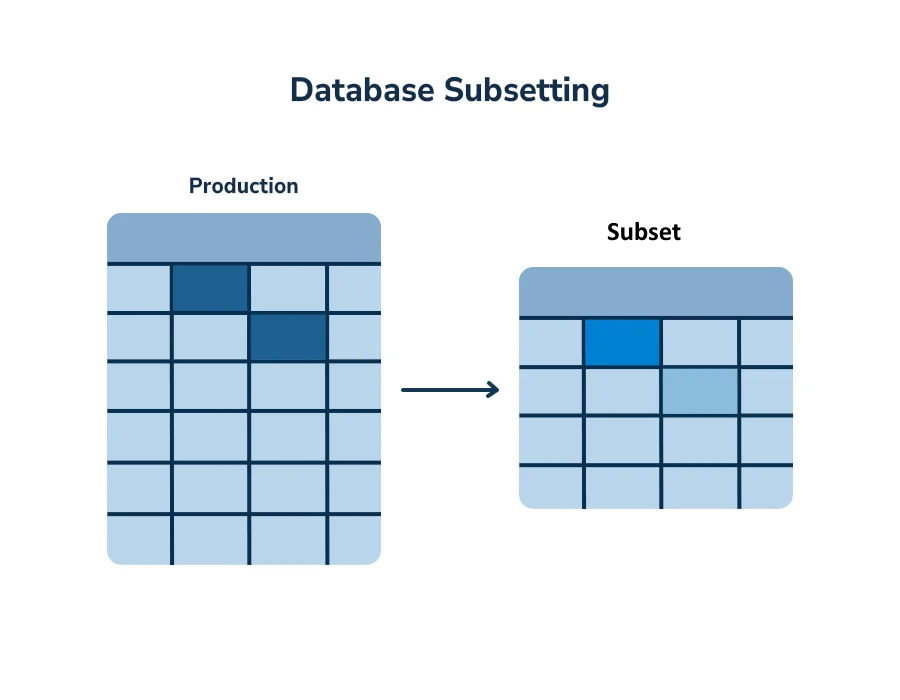
Database Subsetting and Synthetic Data
Subsetted databases populated with synthetic data are important for cross database analytics.
Database subsetting is complex due to several challenges:
-
When selecting a subset of rows from a table, you must also get the rows of related tables.
-
A relational constraint may be on multiple columns (Composite keys). In this case a subset requires rows of related tables using the multiple column constraint.
-
Some tables may have no foreign key columns but may have other tables that have foreign keys referencing the table.
-
Cyclical dependencies. Table A has a foreign key to table B and table B has a foreign key back to table A.
LangGrant solves these challenges with a simple visual interface. Start by specifying a percent of the source database size, with or without bias controls. Windocks subsetting does not write to the source database (the one being subsetted).
Challenges in cross database analytics
Joining data between databases is challenging as column level data rarely matches exactly. Fortunately, subsetting can reduce a multi-terabyte database to megabytes in size, while retaining full relational integrity. Down sized databases are then populated with synthetic data, to provide LLMs with safe context needed for LLM generated cross database analytics.
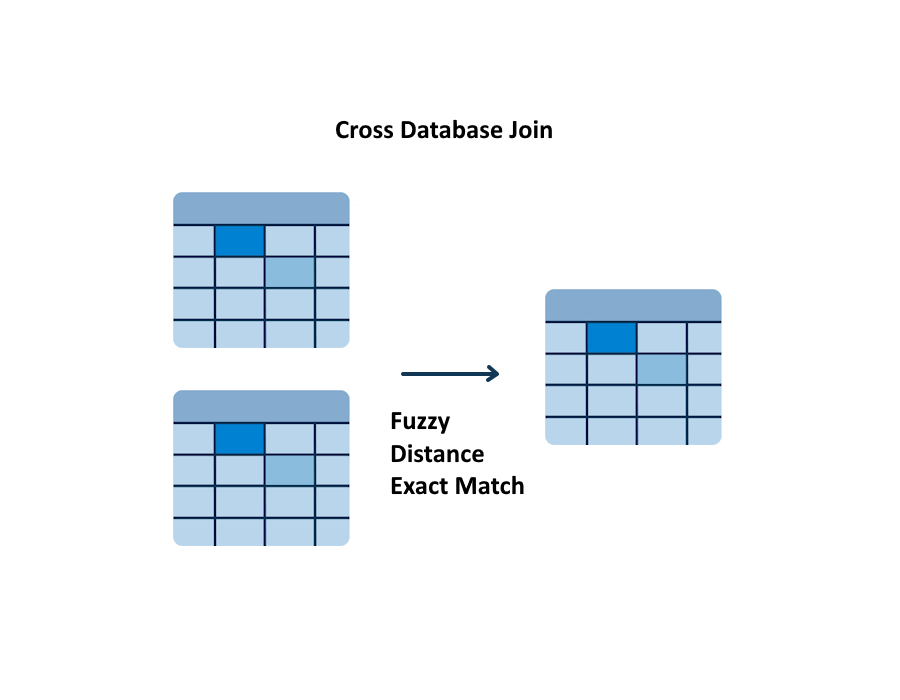
Cross database joins
An LLM provided with a safe synthetically populated database context, is better able to specify a join strategy. LangGrant supports a range of joins, including fuzzy, distance, and exact match.
Explore other LangGrant capabilities
Explore LangGrant capabilities
Orchestration: automated database context
LEDGE automatically delivers complete database context for LLMs to comprehend multiple databases simultaneously at scale. Like a skilled engineer, once an LLM understands databases it can contribute to solution design.
Orchestration: analytic plan
LEDGE binds LLMs to deliver accurate analytic plans for user queries. Plans are saved, easily validated and modified, and run to deliver analytics data within minutes of the user query.
Governance
PII safeguards, authorization controls, data residency rules, firewall restrictions, and token-governance policies are built-in by design. No sensitive data leaves governed systems.
Plan management
LLM generated plans are saved, easily reviewed and validated, modified, and executed, for LLM use that is transparent, explainable, and repeatable.
Database cloning and containers
On demand database clones with containers provide Agent developers with production database copies (with optional masking) for agentic AI dev/test.

Database subsetting and synthetic data
Database subsetting with synthetic data provides added context for working with complex multi-database environments.